Product Roadmap Examples: A Visual Guide
Product roadmap examples aren’t just static documents; they’re dynamic narratives of innovation, charting a course through uncharted waters. They’re the secret weapon for navigating the complex world of product development, transforming abstract ideas into tangible realities. This journey will explore diverse roadmap types, showcasing their strengths and weaknesses, and unraveling the secrets behind successful product launches.
Prepare to be captivated by the power of visual planning and strategic foresight as we delve into the art of crafting compelling roadmaps.
We’ll dissect real-world examples from various industries, revealing the strategic thinking behind each one. We’ll then craft our own hypothetical roadmap for a SaaS project management application, demonstrating how to prioritize features, allocate resources, and adapt to unexpected market changes.
The process will be visually compelling, with infographics and clear explanations, ensuring you leave with the knowledge and inspiration to create your own roadmap masterpiece.
Roadmap Communication and Stakeholder Management
My dear friends, the symphony of product development is not just about crafting a beautiful melody; it’s about conducting a harmonious orchestra of stakeholders. Each instrument – engineering, marketing, sales – plays a crucial role, and their notes must blend seamlessly for the masterpiece to emerge.
Effective communication is the conductor’s baton, ensuring that every section understands its part and plays in perfect time.Effective communication strategies are essential for aligning stakeholders around the product vision. Without clear and consistent messaging, misunderstandings and conflicts can easily arise, derailing the entire project.
This requires a thoughtful approach, tailoring the message to resonate with the unique needs and perspectives of each group.
Communicating the Roadmap to Different Stakeholders
Tailoring communication to resonate with each stakeholder group is paramount. Imagine a painter presenting their masterpiece; they wouldn’t use the same language with a seasoned art critic as they would with a child. Similarly, engineers need detailed technical specifications, while marketing needs compelling narratives to fuel their campaigns.
Sales teams require clear understanding of the product’s value proposition and timeline to effectively engage potential customers. For example, a concise, visually driven presentation might work well for marketing, whereas a detailed technical document would be preferred by the engineering team.
Regular updates, delivered through appropriate channels – email, meetings, dashboards – are key to keeping everyone informed and aligned.
Gathering Feedback and Incorporating it into the Roadmap
Feedback is the lifeblood of a successful product. It’s the audience’s applause, the critic’s review, the whisper of the market. To gather this vital information, we must create channels for open dialogue. This could include regular feedback sessions, surveys, and beta testing programs.
Actively listening to and prioritizing feedback is crucial; this shows respect for stakeholder input and fosters a collaborative environment. For instance, a company might use a dedicated online forum for users to provide feedback on beta releases, which is then analyzed and prioritized by the product team, leading to changes in the roadmap.
Managing Expectations and Addressing Potential Conflicts
The path to product success is not always smooth; conflicts can arise. These moments require skillful navigation, a delicate dance of diplomacy and compromise. Transparency is key; proactively addressing potential issues, even before they escalate, fosters trust and prevents misunderstandings.
Clear communication of priorities, trade-offs, and timelines helps manage expectations. For example, a transparently communicated delay, along with a clear explanation of the reasons and a revised timeline, can mitigate frustration and maintain stakeholder confidence. Furthermore, establishing a clear process for resolving conflicts, such as a formal escalation path, can prevent minor disagreements from becoming major roadblocks.
Remember, my friends, a successful product is built not only on a solid foundation of technology but also on a strong foundation of trust and collaboration.
Measuring Roadmap Success
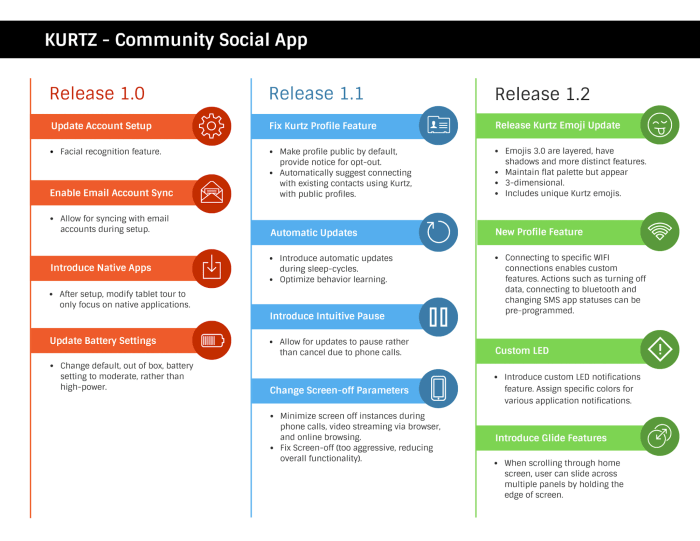
My dear friends, the journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step, and the success of a product roadmap is no different. It’s not enough to simply chart a course; we must diligently measure our progress to ensure we’re truly reaching our destination.
The metrics we choose will illuminate the path ahead, guiding us towards triumph or prompting necessary course corrections. Let us delve into the art of measuring our roadmap’s effectiveness.Key Metrics for Evaluating Roadmap Effectiveness are vital indicators of our progress.
They provide the necessary insights to steer our ship towards success. Without a clear understanding of what constitutes success, we risk drifting aimlessly. Choosing the right metrics allows us to objectively assess our performance and make data-driven decisions.
Key Metrics for Roadmap Evaluation
A well-chosen set of metrics provides a comprehensive view of roadmap performance. These metrics should align directly with the overall strategic goals and objectives defined for the product. For example, if the primary goal is market share growth, then metrics such as customer acquisition cost and market penetration would be critical.
Conversely, if the focus is on improving customer satisfaction, Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer churn rate would be more relevant. We must select metrics that are measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments
Regular monitoring of our chosen metrics is paramount. This involves establishing a consistent tracking system, which might include using project management software or creating custom dashboards. Visual representations of progress, such as Gantt charts or burn-down charts, can offer a clear picture of where we stand against our planned timeline.
If deviations from the plan emerge, it is crucial to analyze the root causes. Are there unforeseen challenges? Have market conditions shifted? By understanding the reasons behind deviations, we can make informed decisions about necessary adjustments to the roadmap.
This might involve prioritizing features differently, reallocating resources, or even adjusting the timeline.
Using Roadmap Data to Inform Future Decisions, Product roadmap examples
The data collected from tracking our roadmap’s progress is invaluable for future product development. By analyzing the performance of individual features and initiatives, we can identify patterns and insights that inform future strategies. For example, if a specific feature significantly exceeded expectations in terms of user engagement, we might consider investing more resources in similar features in the future.
Conversely, if a feature underperformed, we can learn from its shortcomings and avoid repeating similar mistakes. This iterative process of learning and adaptation is key to creating successful products and refining our roadmap over time. It’s a continuous cycle of refinement, driven by data and informed by experience.
Final Wrap-Up: Product Roadmap Examples
From strategic visions to tactical execution, mastering the art of the product roadmap is key to navigating the ever-evolving landscape of product development. We’ve journeyed through diverse examples, dissected successful strategies, and even built our own roadmap from the ground up.
Remember, a roadmap isn’t just a plan; it’s a living document that evolves alongside your product and your understanding of the market. Embrace the iterative process, gather feedback, and use your roadmap as a powerful tool to guide your team toward success.
Now go forth and create your own epic journey!

